The Behavioral State Model is a model of behavior that I’ve been developing for a number of years.
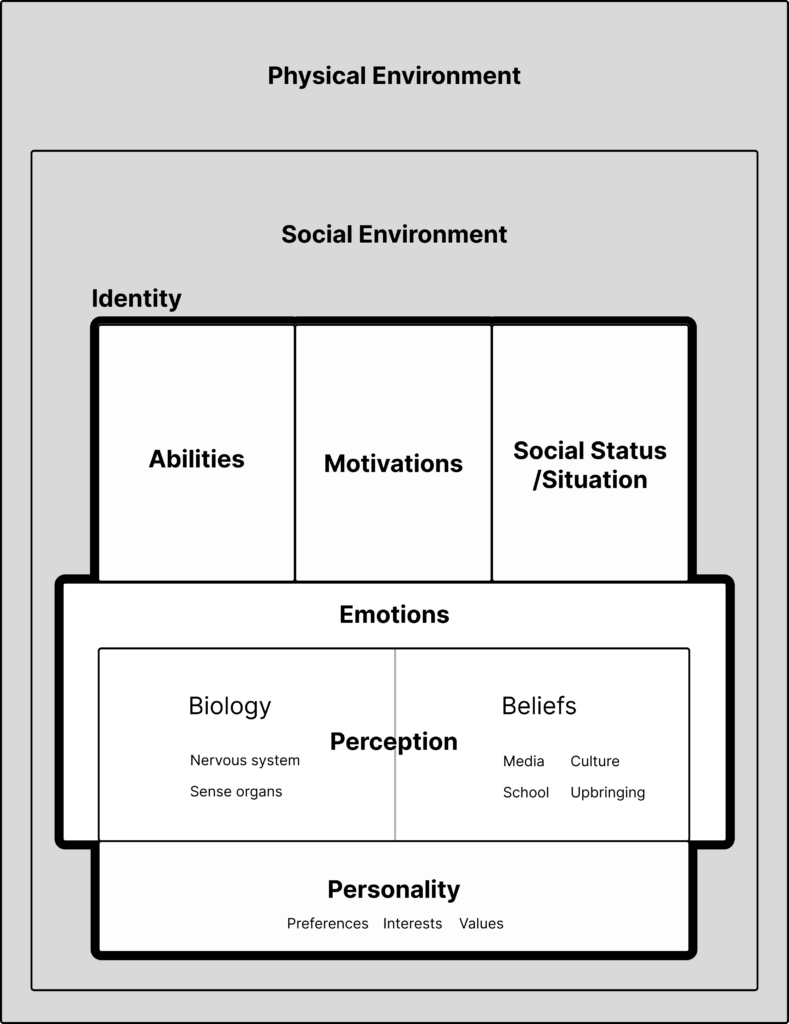
The basic idea is that at any moment in time we are in a particular “Behavioral State”. This state is determined by:
- Our personality
- Our perception
- Our emotions
- Our abilities
- Our social status/situation
- Our motivations
- Our social environment
- Our physical environment
The first 6 items together make up our identity:
- Identity = Personality + Perception + Emotions + Abilities + Social Status/Situation + Motivations
And the perception component can be broken down into two subcomponents:
- Perception
- Biology
- Beliefs
In every moment, we are in a particular Behavioral State. The Behavioral State we’re in makes certain actions more likely and certain actions less likely.
For example, if in the current moment we have a low ability to exercise, or have a belief that exercising is a waste of time, our current Behavioral State will make that behavior unlikely.
At any given moment in time, a Behavioral State Score can be calculated for any given behavior. This score is determined by all of the different components:
- Behavioral State Score for (specific behavior)
- Personality: Is this person interested in this specific behavior? Does it fit into their value system? Does it match their preferences?
- Perception: Does this person believe that this specific behavior is fun, interesting, helpful, etc? Do they even think it’s possible? Do they have the perceptual ability to partake?
- Emotions: Is this person in an emotional or unemotional state? If they’re in an emotional state, are they in the right emotional state for this behavior to occur?
- Abilities: Does this person have the ability to perform this specific behavior? Do they have a special talent for this specific behavior?
- Social Status/Situation: Does this person’s social position encourage this specific behavior? Will this specific behavior increase or decrease their social status?
- Motivations: Is this person motivated to perform this specific behavior? Is there a reward or incentive for doing this specific behavior?
- Social Environment: Is there a social norm/social pressure for this specific behavior in their current context?
- Physical Environment: Is it possible to perform the specific behavior in this current physical environment?
If any component is insufficient for a particular behavior, it will not occur.
The Behavioral State Model also gives Behavioral Designers and applied behavioral scientists a framework they can use to change behavior. In order to get someone to behave differently, you first need to understand their Behavioral State and which components are lacking. By doing a Behavioral State Analysis you can determine the most effective way of changing the behavior in question.
The Behavioral State Model also provides Behavioral Designers with a variety of different levers they can pull to modify behavior. The Behavior State Model has eight behavioral modifiers, where the other popular models in the field have three:
- The Behavioral State Model
- 8 Behavioral Modifiers
- Personality
- Perception
- Emotions
- Abilities
- Social status/situation
- Motivations
- Social environment
- Physical environment
- 8 Behavioral Modifiers
- The Fogg Behavior Model
- 3 Behavioral Modifiers
- Motivation
- Ability
- Trigger
- 3 Behavioral Modifiers
- COM-B Model
- 3 Behavioral Modifiers
- Capability
- Opportunity
- Motivation
- 3 Behavioral Modifiers
In addition, the Behavioral State Model incorporates cognitive factors (like perceptions and beliefs) and personality. These are important determinants of behavior that are missing from other behavior change models.





